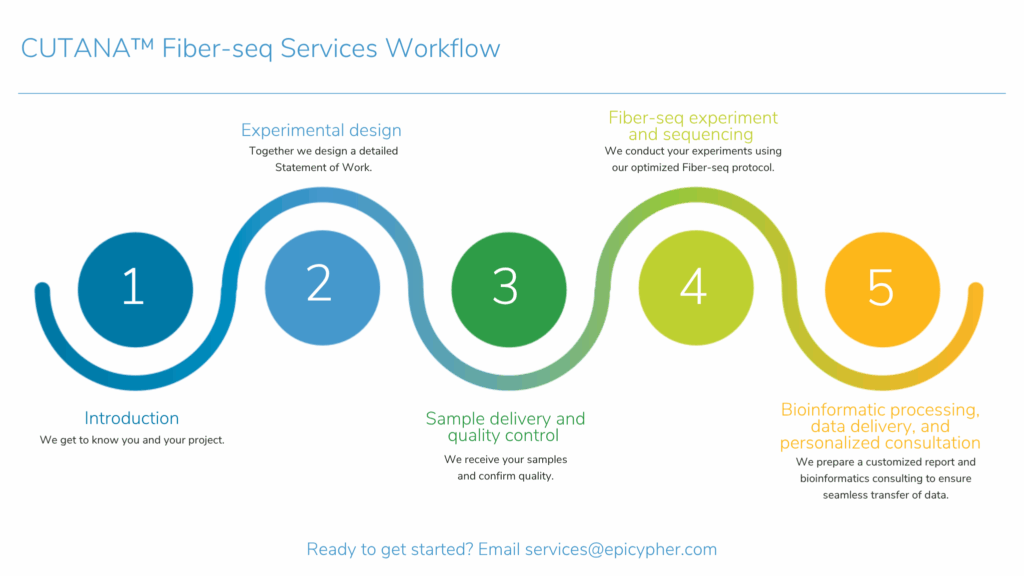
CUTANA™ Fiber-seq Assay Services for Long-Read Sequencing
EpiCypher’s CUTANA™ Fiber-seq Services provide biotech and academic researchers with unique access to our genomic expertise and multiomic capabilities, enabling diverse applications across biomedical research and drug development.
Taking advantage of EpiCypher’s Fiber-seq services gives you expert access to single-molecule, multiomic profiling of chromatin accessibility, DNA methylation, and DNA sequence.
By integrating these layers of information using long-read sequencing, Fiber-seq delivers insights far beyond what is possible with conventional approaches like ATAC-seq or bisulfite sequencing.
As our partner, you can expect to:
- Accelerate Your Research – Get expert guidance from design to analysis, ensuring fast and reliable adoption of Fiber-seq in your studies.
- Do More with One Assay – Unlock chromatin accessibility, DNA methylation, and genetic variation in a single experiment, saving time and resources.
- See What Others Miss – Achieve single-molecule resolution across challenging genomic regions beyond the reach of short-read technologies.
- Drive Translational Applications – Directly link chromatin regulation to underlying disease variants.
- Turn Data into Discovery – Gain biological insights with curated reports and direct consultation from our genomic scientists to drive your next breakthrough.

Ready to Get Started?
Tell us briefly about your project, and a member of our Services team will get back to you shortly!
About CUTANA™ Fiber-seq Assay
Fiber-seq is a novel multiomic mapping assay that leverages DNA methyltransferase (MTase) Hia5 to label open chromatin with N6-methyladenosine (6mA). Unlike existing assays that require chromatin fragmentation, this approach preserves the DNA molecules intact for long-read sequencing (LRS).
Fiber-seq is the first commercially available chromatin accessibility assay that leverages long-read sequencing. In Fiber‑seq, nuclei are isolated and then incubated with Hia5 6mA MTase. The cofactor for Hia5, S‑adenosylmethionine (SAM), is added, which activates the Hia5 to induce methylation of adenines within accessible chromatin in as short as 10 minutes. Following, the enzyme is quenched, high molecular weight (HMW) DNA is purified, and the sample is prepared for LRS following standard protocols.
Our Services team is highly skilled at performing the Fiber-seq assay and data analysis, and is ready to help you get started with your experiment!
Fiber-seq unravels multiple layers of chromatin regulation
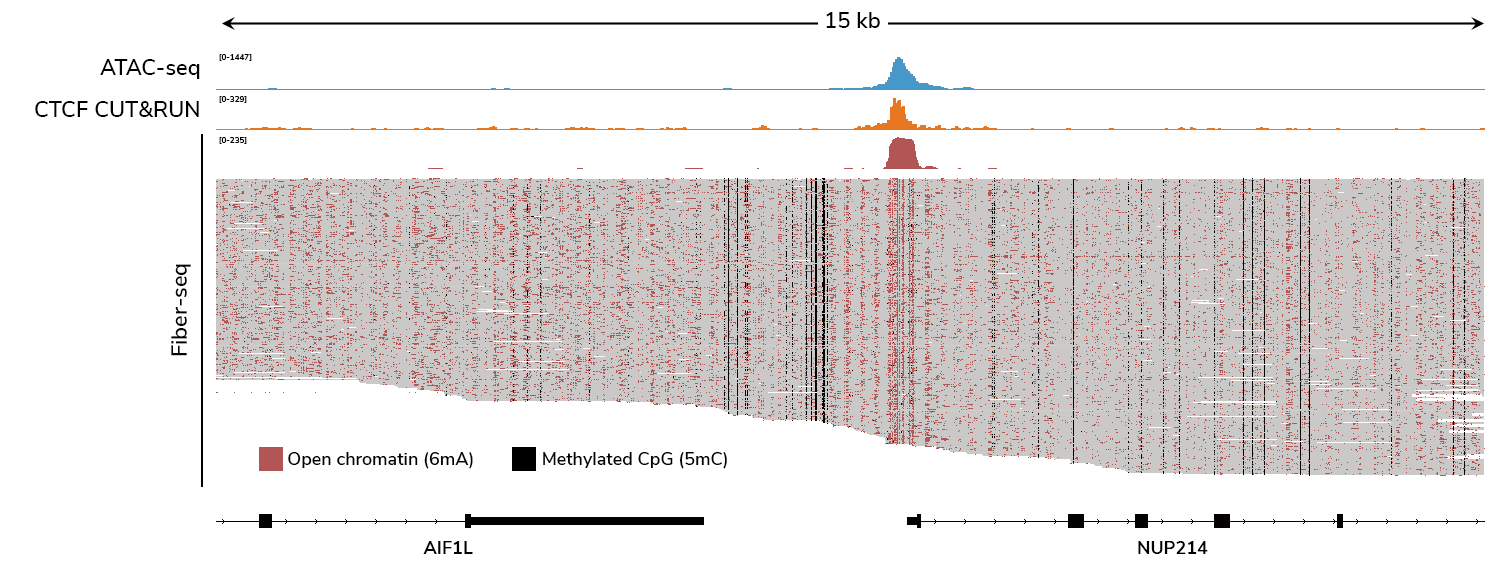
CUTANA™ Fiber-seq simultaneously detects open chromatin (marked by N6-methyladenine; 6mA) and DNA methylation (5mC) in human leukemia (K562) cells. ATAC-seq and CTCF CUT&RUN data are shown for comparison. Each horizontal line in the Fiber-seq panels represents a single long read, providing single-molecule data. Data from 60 individual DNA molecules are shown.
Fiber-seq detects protein footprints genome wide
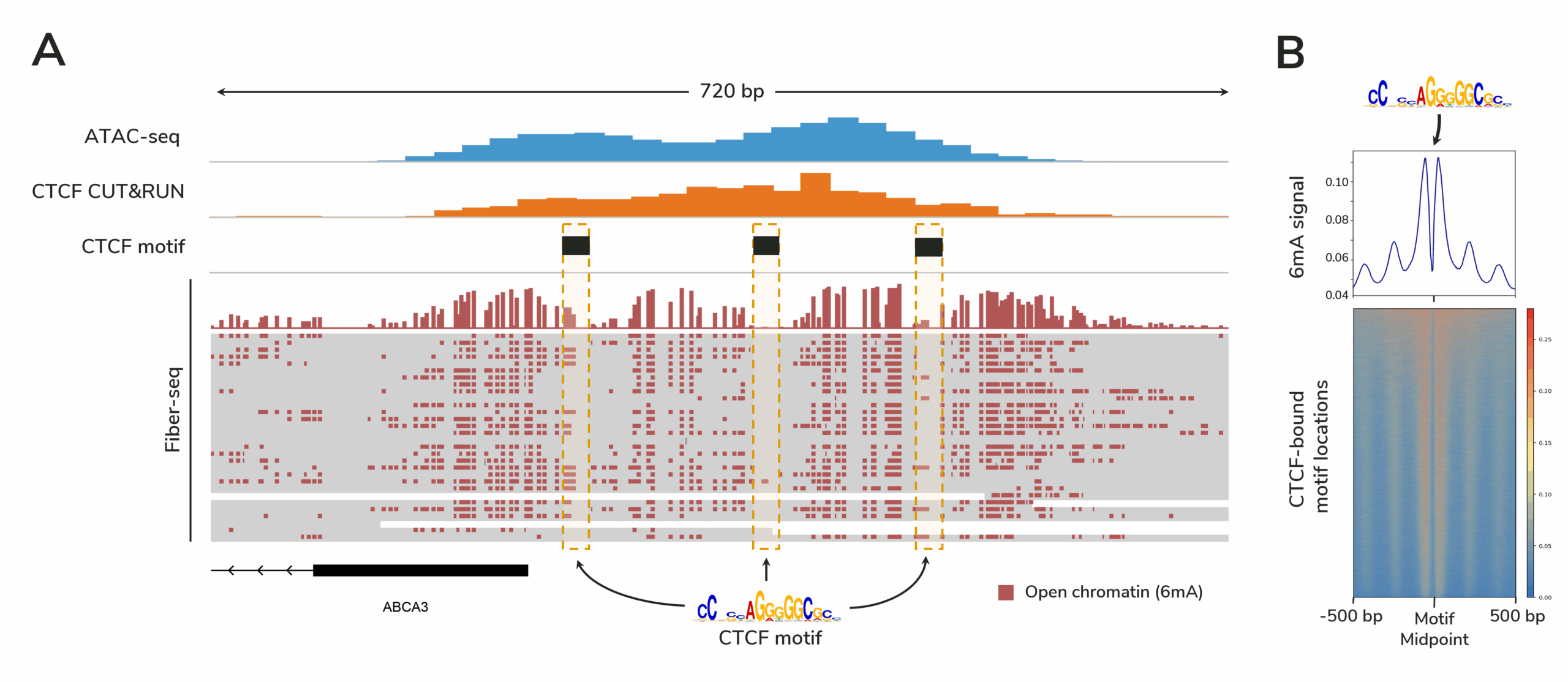
Figure Caption
(A) Fiber-seq data from 30 individual DNA molecules are shown, with the top track displaying aggregate 6mA signal marking open chromatin. Each horizontal line below this track represents a single DNA molecule. Dotted boxes indicate CTCF motif regions. Because Fiber-seq provides single-molecule resolution, heterogeneity in protein binding across the cell population is revealed (the leftmost boxed region shows variable 6mA labeling, suggesting differential CTCF occupancy).
(B) Genome-wide 6mA signal from this Fiber-seq experiment demonstrates robust footprinting of CTCF sites. Elevated 6mA levels flanking the motif midpoint reflect accessible DNA surrounding CTCF binding sites.
Why Consider CUTANA™ Fiber-seq Services?
What can you achieve by using CUTANA™ Fiber-seq services?
Leverage EpiCypher’s Fiber-seq services to achieve:
Multiomic insights in one assay – Fiber-seq simultaneously profiles chromatin accessibility, DNA methylation, and genetic variants, consolidating what typically requires three or more separate assays into one long-read sequencing assay.
Highest activity 6mA-MTase – Faster labeling via Hia5 enables higher resolution of accessible DNA, with demonstrated utility in protein footprinting applications to resolve transcription factor binding and nucleosome positioning [2-4].
Access complex genomic regions – Profile chromatin accessibility in repetitive and structurally complex regions such as transposable elements, centromeres, telomeres, segmental duplications, and chromosomal rearrangements.
Resolve chromatin state heterogeneity – PCR-free approach leverages long-read sequencing to directly profile individual DNA molecules, uncovering heterogeneity of complex cell populations often missed by short-read techniques.
What are the service applications?
- Resolve rare disease – Link genetic variants to gene regulatory changes to uncover mechanisms of Mendelian disorders
> https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/39880924 - Profile brain epigenomics – Map cell-type-specific chromatin architecture in the human brain
Unravel complex immunology – Identify haplotype-selective chromatin accessibility in immune cells
> https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/40501892Track transcriptional dynamics – Monitor RNA polymerase activity and its effects on chromatin structure
Explore plant biology – Reveal hidden regulatory elements in highly repetitive crop genomes
Illuminate centromeres – Characterize conserved chromatin organization in repetitive centromeric regions across species
Publications and Technical Notes
- Stergachis et al. Science (2020). PMID: 32587015
- Tullius et al. Mol. Cell (2024). PMID: 39191261
- Dubocanin et al. Cell Genom. (2025). PMID: 40147439
- Vollger et al. bioRxiv (2024). DOI: 10.1101/2024.06.14.599122
- Jha et al. Genome Res. (2024). PMID: 38849157
For detailed technical information about the Fiber-seq assay please see the Fiber-seq protocol.