Low inputs. Reduced costs. Superior data quality.
CUTANA™ ChIC / CUT&RUN assays leverage recent advancements in immunotethering technologies to deliver efficient, ultra-sensitive chromatin mapping capabilities. Compared to ChIP-seq, the leading assay for epigenomic profiling, CUT&RUN offers clear advantages:
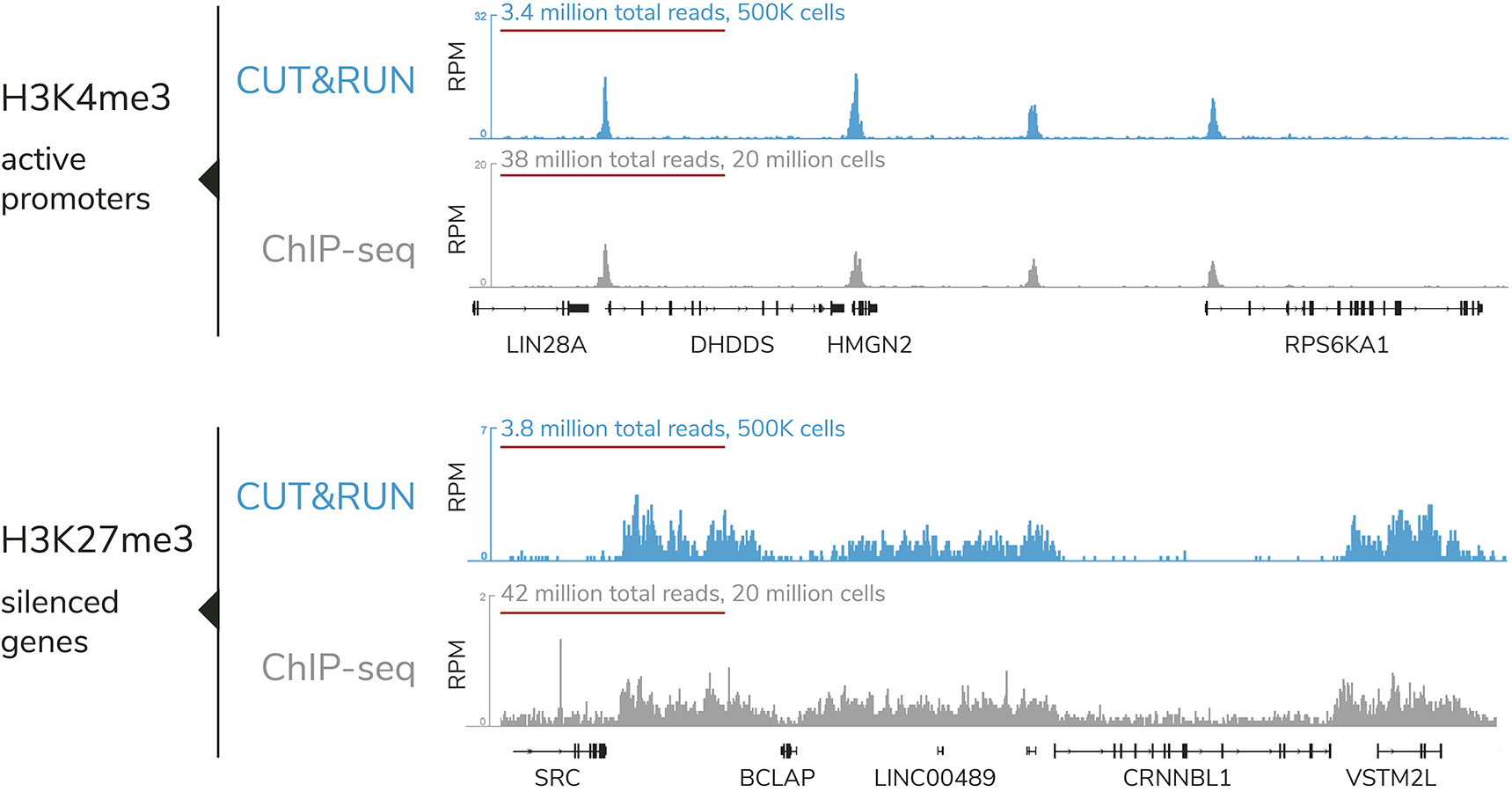
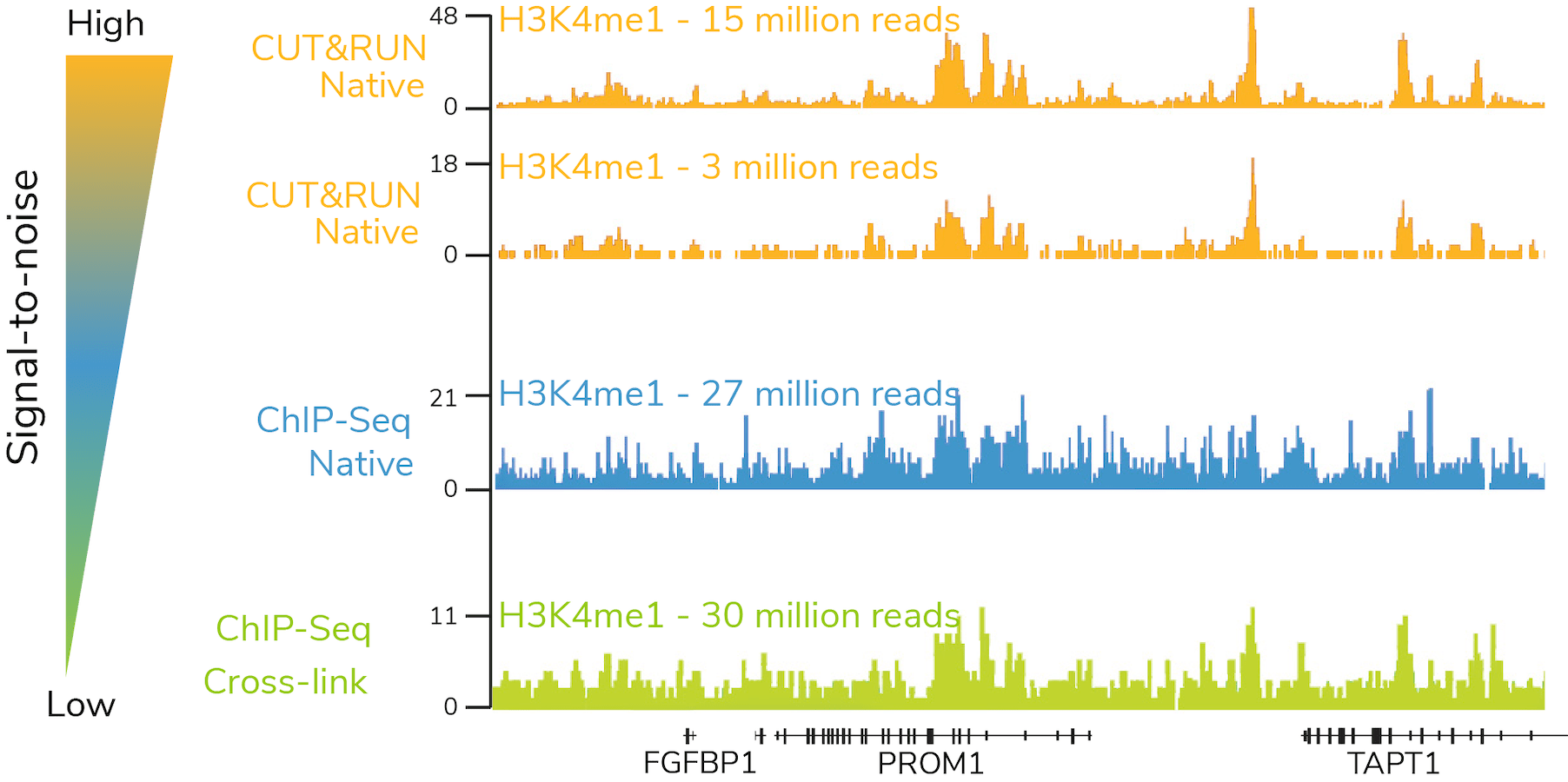
- High signal-to-noise at reduced sequencing depth
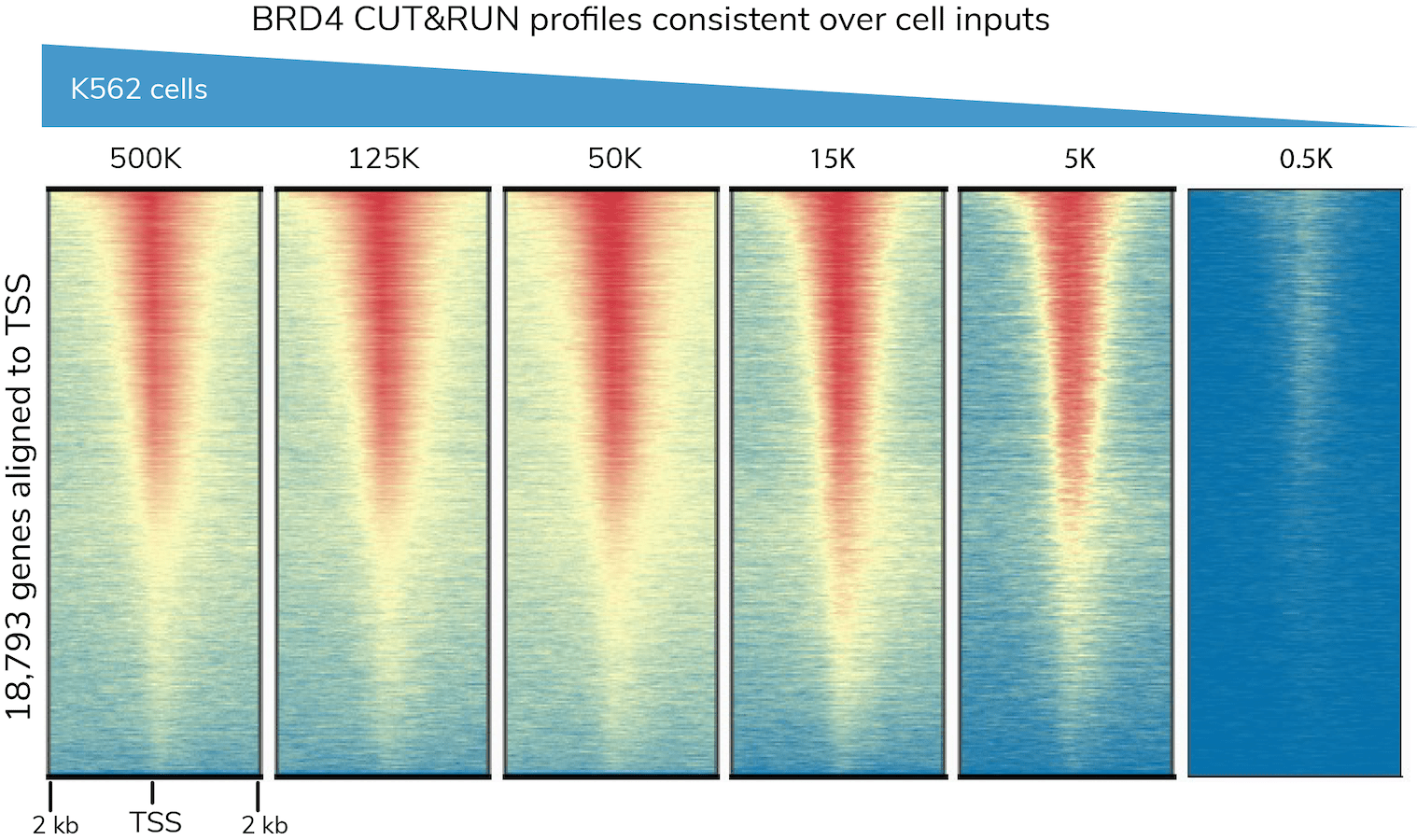
- Low cell input requirements
- Diverse sample inputs and targets
- Streamlined, cost-effective workflow
- Go from cells to sequencing using our CUT&RUN and Library Prep Kits
Have Questions?
We’re here to help. Click below and a member of our team will get back to you shortly!
Request More InfoHow does CUT&RUN work?
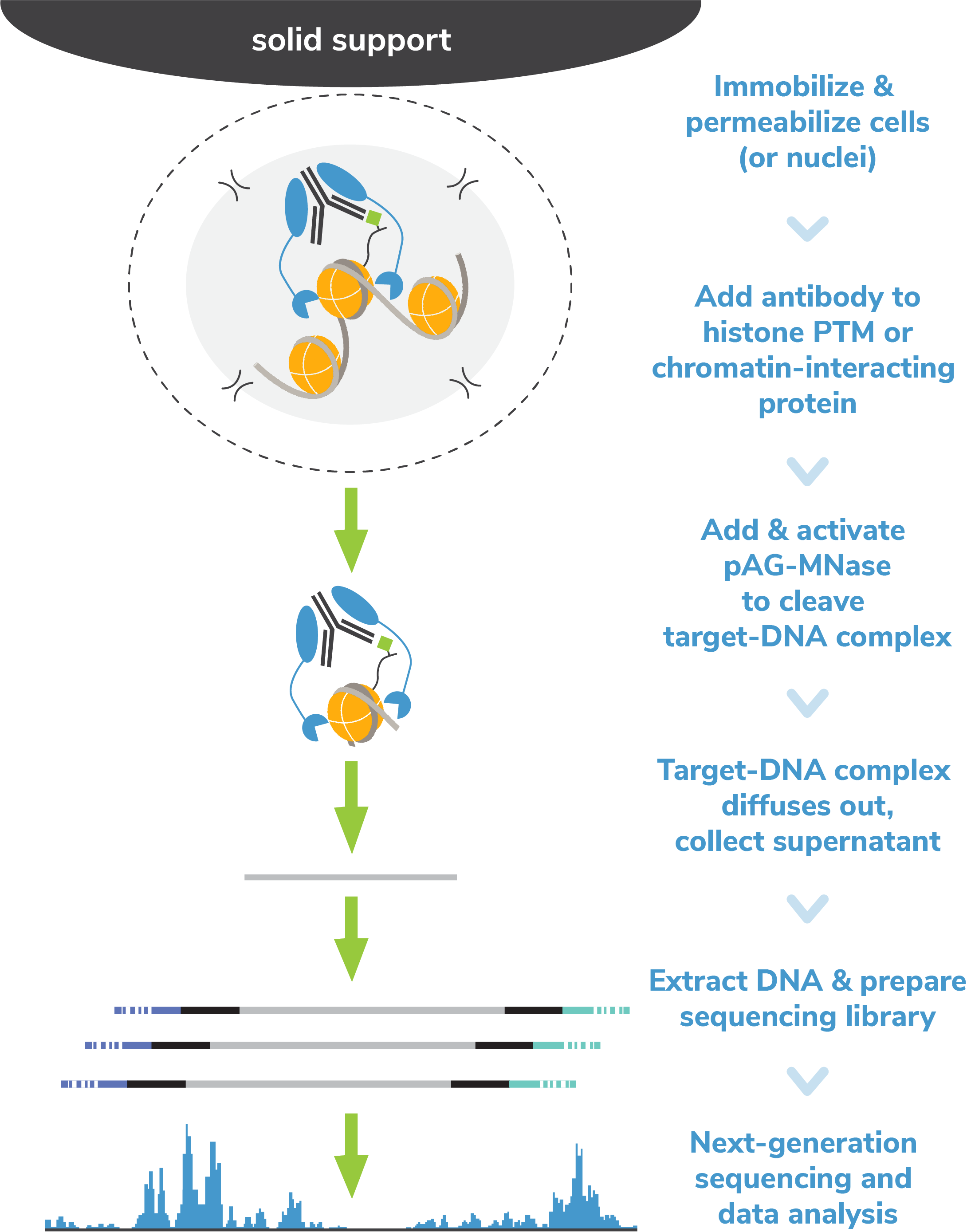
The Cleavage Under Targets and Release Using Nuclease (CUT&RUN) method builds upon Chromatin ImmunoCleavage (ChIC) technology.
In CUT&RUN, a fusion of protein A, protein G and micrococcal nuclease (pAG-MNase) is used to selectively cleave antibody-labelled chromatin. This strategy eliminates immunoprecipitation steps, greatly simplifying the assay workflow. Clipped chromatin fragments are isolated from solution and used for NGS.
The targeted enrichment of CUT&RUN allows for better signal : noise with only 3-5 million sequencing reads, significantly reducing sequencing costs vs ChIP-seq. See a video summary of CUT&RUN advantages here.
Want to get started? Our CUT&RUN and Library Prep Kits provide a comprehensive and streamlined solution.
To learn more about CUT&RUN, check out our Technical Support Center.
CUTANA™ CUT&RUN: Go from cells to data in < 4 days
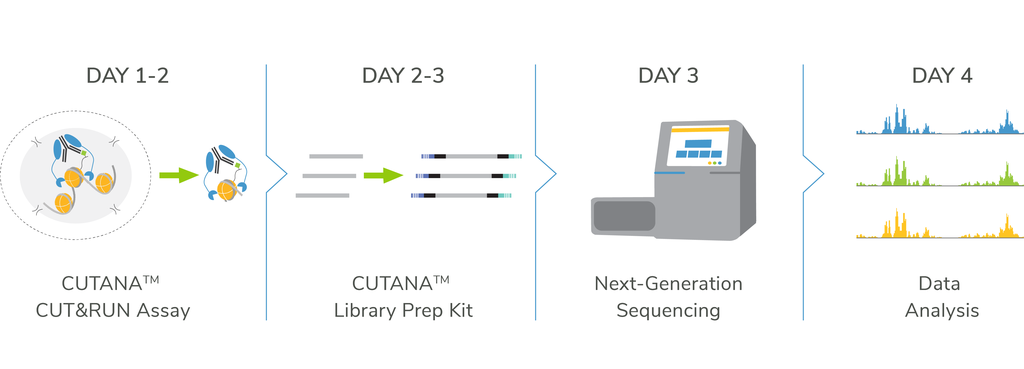
Get started with CUTANA™ CUT&RUN assays
CUTANA™ CUT&RUN Kit & pAG-MNase
Jumpstart your chromatin profiling studies with our user-friendly CUT&RUN Kit or customize your workflow using pAG-MNase and our DIY protocol. For robust sequencing data, add the CUT&RUN Library Prep Kit.
CUTANA™ CUT&RUN Antibodies
EpiCypher’s CUTANA™ Antibodies are rigorously tested for reliable and robust performance in CUT&RUN assays. Check out our available chromatin-associated protein and histone PTM antibodies.
CUTANA™ CUT&RUN Services
Our CUT&RUN Services provide unique access to our genomics experts, automated CUT&RUN workflows, and in-house bioinformatic pipelines. Perfect for pilot experiments and high-throughput studies alike.
The CUTANA™ CUT&RUN Protocol
EpiCypher offers a collection of products for CUT&RUN assays, including pAG-MNase, spike-in controls, antibodies, and accessory reagents / tools, making it easy to create your own assay or follow a standard protocol.
We have developed a reliable and user-friendly CUT&RUN protocol, optimized for:
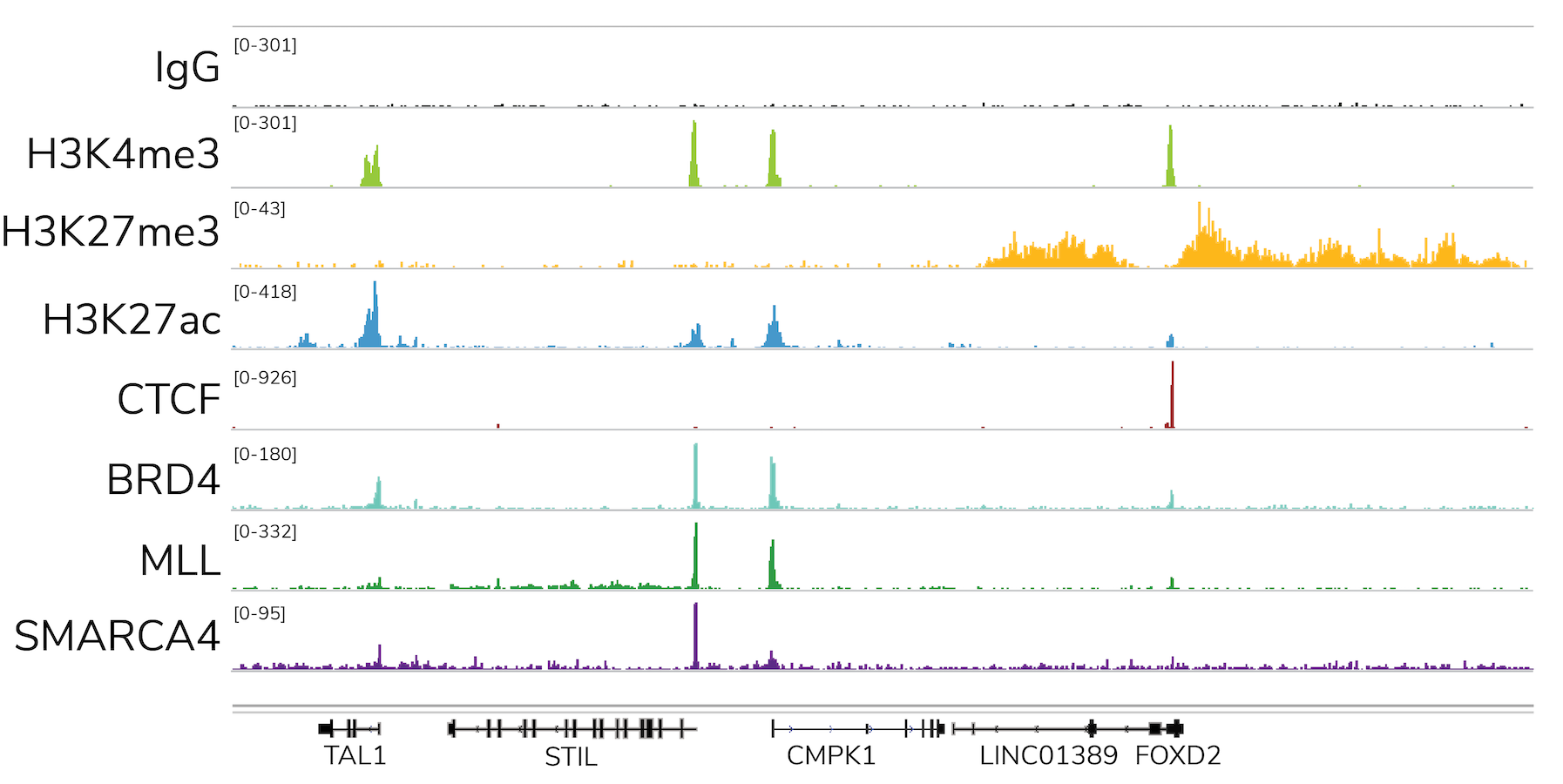
- Diverse targets, including histone PTMs, transcription factors, and more
- Low cell inputs (down to 5,000 cells)
- Reduced sequencing depths (3-5 million sequencing reads)
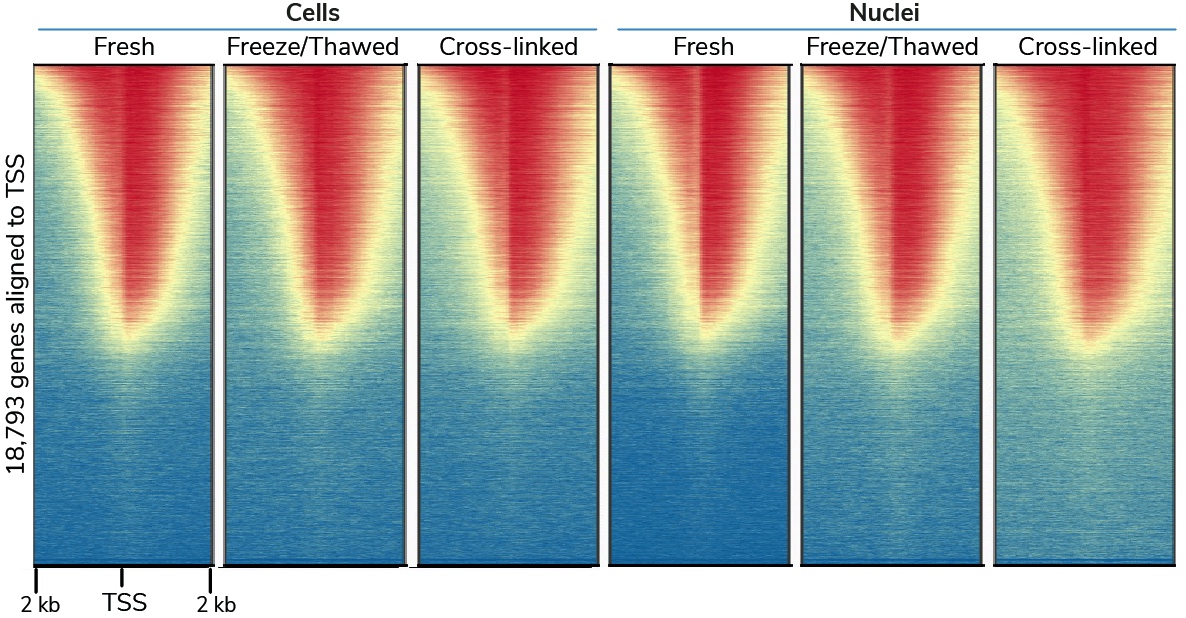
- Fresh, frozen, and cross-linked cells or nuclei
In addition, we have addressed common issues (e.g. bead clumping / loss) and enabled high-throughput sample handling via an 8-strip format. The protocol includes notes throughout, critical steps, pictures for clarity, and a FAQ section.
Above is a comprehensive walkthrough video put together by our scientific and technical support team to compliment our CUT&RUN protocol.
View our ProtocolFeatured Publications
Skene and Henikoff. An efficient targeted nuclease strategy for high-resolution mapping of DNA binding sites. eLife 6, e21856 (2017). (PMID: 28079019)
In 2017, Steven Henikoff’s lab at the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center published their first paper describing CUT&RUN. This in situ chromatin mapping assay builds on ChIC technology from Ulrich Laemmli’s group, using a protein A-fused micrococcal nuclease (pA-MNase) to selectively cleave antibody-bound chromatin loci in intact cells and nuclei. Skene et al. describes the assay and uses it to profile several transcription factors in yeast and human nuclei. Head-to-head comparisons with ChIP-seq assays further highlights the enhanced sensitivity, improved signal : noise, and reduced sequencing requirement of CUT&RUN vs. leading assays.
Meers et al. Improved CUT&RUN chromatin profiling tools. eLife 8, e46314 (2019). (PMID: 31232687)
This 2019 paper from the Henikoff lab reports the development of a novel protein A-protein G fused micrococcal nuclease (pAG-MNase), for use in CUT&RUN. pAG-MNase expands antibody species compatibility in CUT&RUN assays and forms the basis for EpiCypher’s CUTANA CUT&RUN technology. This paper also describes the use of E. coli DNA for assay calibration and a modified MNase digestion strategy for improved yield with minimal background, representing significant breakthroughs for CUT&RUN assays.
Yusufova et al. Histone H1 Loss drives lymphoma by disrupting 3D chromatin architecture. Nature AOP (2020). (PMID: 33299181)
Linker histone H1 proteins are important components of chromatin structure and are frequently mutated in B-cell lymphoma, but their role in cancer development has been unclear. Here, Yusufova et al. establish H1 as a bona fide tumor suppressor protein, demonstrating that H1 mutations alter chromatin structure to support re-expression of developmental genes and subsequent cancer development. EpiCypher’s use of CUTANA CUT&RUN technology to examine changes in H3K9me2 and H3K9me3 was key to uncovering this complex mechanism.
Wilson et al. ARID1A mutations promote P300-dependent endometrial invasion through super-enhancer hyperacetylation. Cell Rep. 33, 108366 (2020). (PMID: 33176148)
ARID1A is a key subunit of the SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complex and is commonly mutated in severe forms of endometriosis; however, its function is not well defined. Here, Wilson et al. show that ARID1A co-localizes with and represses the p300 lysine acetyltransferase. Mutation of ARID1A results in increased H2K27ac at super-enhancers and supports invasive endometrial growth. To profile H3K27ac at super-enhancers, Wilson et al. applied EpiCypher’s CUTANA pAG-MNase for ultra-sensitive CUT&RUN assays.
Stengel et al. Definition of a small core transcriptional circuit regulated by AML1-ETO. Mol Cell AOP (2020). (PMID: 33382982)
Chromosomal translocations in cancer can result in fusions of transcription factors to other protein domains, altering gene expression to drive oncogenesis. In acute myeloid leukemia (AML), the most common fusion protein is AML-ETO, combining the DNA binding domain of AML/RUNX1 to the transcriptional corepressor ETO. Here, Stengel et al. performed a comprehensive analysis of AML-ETO function, utilizing PRO-seq, CRISPR-based mutagenesis, and EpiCypher CUT&RUN technology to define AML-ETO targets and downstream effects.
To see a full list of publications, click here.